On November 15 in 2022, the United Nations (UN) reported that the number of people on Earth had grown to eight billion (8,000,000,000). That came just 11 years after the world reached seven billion people. The world faces challenges ahead as the population continues to grow.
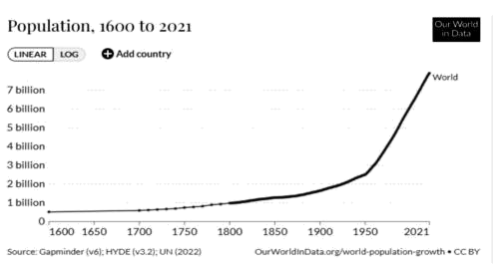
The world’s population – the number of people on the planet – has grown rapidly over the last 200 years. In 1805, for the first time ever, the Earth had a billion people on it. It took over 100 years for that number to double to two billion. In less than 50 years, it had doubled again to four billion. Now, again in less than 50 years, the number has doubled once more to eight billion.
How fast local populations are growing depends a lot on where you are in the world. Typically, as countries become richer, their population growth slows. In some countries, like Japan, the number of people is actually shrinking. The greatest population growth these days is found in Asia and Africa.
Currently, China, with a population of 1.4 billion, is the country with the most people. That’s expected to change in the next year, when experts say India will pass China as the country with the world’s largest population. Other countries where rapid growth is expected through 2050 are the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, and Tanzania.
【小题1】When did the world’s population reach 7 billion?| A.In 2022. | B.In 2011. | C.In 1905. | D.In 1805. |
| A.Japan’s population is increasing sharply. |
| B.Pakistan’s population keeps dropping slowly. |
| C.A country’s population completely relies on its richness. |
| D.The world’s population is growing more rapidly since 1950. |
| A.China. | B.Nigeria. | C.India. | D.Egypt. |